Exploring the different types of management styles
This article was updated on April 18, 2024.

Written by Michael Feder

Reviewed by Kathryn Uhles, MIS, MSP, Dean, College of Business and IT
Whether someone is interested in becoming an entrepreneur or simply pursuing a business degree, they’ll likely use one or more of several management styles during their career. Understanding management tactics can help in many capacities, from learning how to lead and manage people more effectively as a team to fostering a more positive experience on group projects for school and work. Explore different leadership styles that can be implemented in management positions.
What is a management style?
A management style describes the method and approach a manager uses to motivate, direct and oversee their team. It encompasses decision-making; planning and organization; and interaction with employees. Different styles have unique effects on team dynamics, productivity and culture. For managers, adopting the style that best fits their team and organizational goals is crucial.
Eight types of management styles
There are a wide variety of leadership styles, and the leadership characteristics that a manager chooses to employ are important. Applying the wrong one to the wrong team can lead to miscommunication at best and organizational disaster at worst. Consider how the following eight management types fit both a manager's personality and that of the team they lead.
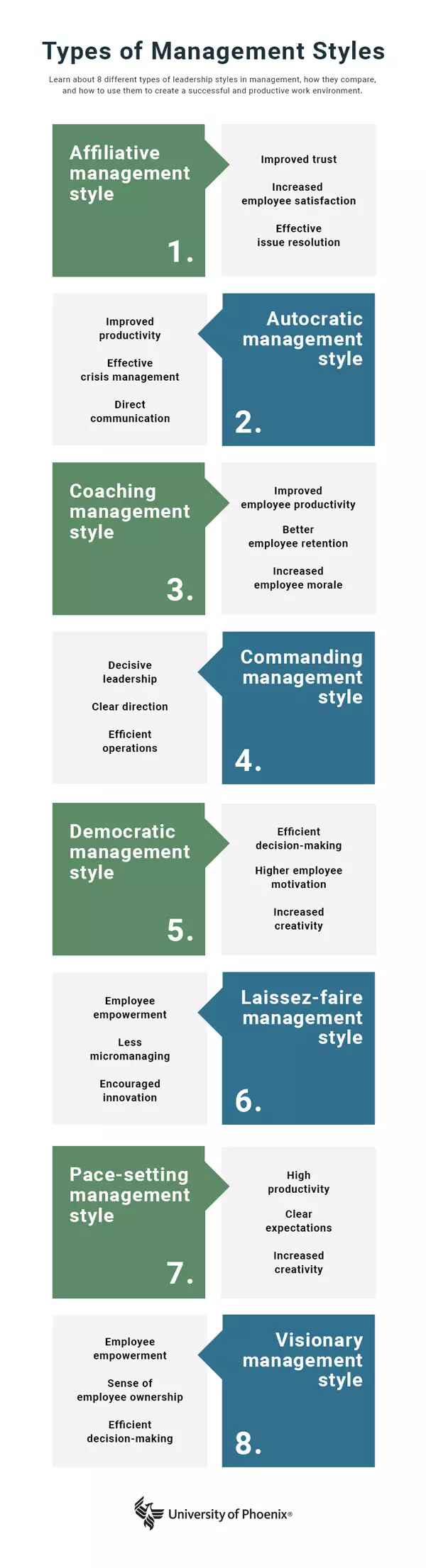
1. Affiliative
Affiliative management focuses on creating and maintaining positive relationships within the team. Consider it a "people first" approach. Affiliative management encourages team-building exercises and aims to make everyone feel comfortable and appreciated. The overall goal is to promote cooperation and harmony.
The advantages of affiliative management include:
- Improved trust: Managers who use this style try to foster trust among their team members. When people feel comfortable with each other, morale and loyalty increase.
- Increased employee satisfaction: Employees who feel appreciated and a part of a team may be more productive and satisfied.
- Effective issue resolution: By focusing on building positive relationships, this approach is conducive to efficient and effective conflict resolution.
The disadvantages of affiliative management are:
- Complacency: When employees receive consistently positive feedback from managers, they may become less motivated to challenge themselves to grow.
- A lack of focus: Some employees require direct and specific leadership and can become stressed by the hands-off style of this approach.
- Ineffective crisis management: While affiliative managers are good with people, they may falter in the face of crises requiring immediate attention.
Every organization may want to consider having an affiliative leader to enhance the workplace.
2. Autocratic
Autocratic leadership is the opposite of affiliative management. This style hinges upon control and power, with decision-making resting entirely in the hands of one person: the manager.
Generally, autocratic managers take charge of day-to-day operations and provide each team member with precise instructions. These bosses might frequently check on the team's progress to ensure everything is on schedule.
The advantages of autocratic management include:
- Improved productivity: Autocratic leaders outline clear expectations for employees when delegating tasks. They hold team members accountable for timely goal completion. As a result, productivity may increase.
- Effective crisis management: In times of crisis or emergency, autocratic managers are quick to take charge and make crucial decisions.
- Direct communication: Autocratic managers communicate directly with their employees, providing clear instructions. This eliminates any confusion and ensures everyone is on the same page.
The disadvantages of autocratic management include:
- Lack of employee input: Employees cannot share their thoughts or ideas, potentially leading to frustration.
- Ineffective team building: Autocratic management often lacks team building, as employees are less likely to work together closely.
- Micromanagement: This style may lead to overly intense attention on employees’ actions and responsibilities, which can be highly frustrating for employees.
While this style may not be suitable for all workplaces, it can be successful for managers who have a clear vision and a firm commitment to deadlines as well as a team that thrives under directive management.
3. Coaching
A coaching style leader builds a strong connection with employees and helps them improve their professional skills and abilities through one-on-one guidance. Team members are encouraged to experiment with new ideas while meeting company targets.
The advantages of coaching management include:
- Improved employee productivity: Coaching managers can help employees improve their professional skills, which can lead to increased productivity.
- Better employee retention: When employees feel that they are being coached and developed professionally, they are more likely to stay with the company.
- Increased employee morale: Employees who receive guidance and support from their managers often have higher morale.
The disadvantages of coaching management include:
- Ineffective when employees are unreceptive to guidance: Coaching management requires buy-in from both the leader and the employee.
- Time requirement: Coaching managers must spend considerable time with each employee to understand them and how best to guide them.
- Additional training may be necessary: Coaching managers often need to be trained in giving feedback and developing employees' skills.
The coaching style of management might be ideal for employees who want to improve their professional skills and managers who can commit to helping them get there.
4. Commanding
This type of boss is often a strong leader who makes quick decisions and expects team members to follow orders. It is a common method for influencing employee behavior.
The advantages of commanding management include:
- Decisive leadership: A commanding manager makes quick decisions, which can be helpful in difficult situations.
- Clear direction: Employees know precisely what is expected of them.
- Efficient operations: This type of management sometimes leads to more efficient operations, as employees can work without interference.
The disadvantages of commanding management include:
- Higher employee stress: Employees who work under a commanding manager may often feel anxious because of the pressure to perform, especially when the manager may be a perfectionist or taskmaster with unreasonable expectations.
- Lack of creativity: Employees may hesitate to share ideas or challenge the status quo under a commanding manager, which can hinder personal and company growth.
- Resistance from employees: Employees may push back on following orders from a commanding manager, leading to tension and conflict.
The commanding style of management might be best suited for employees looking for decisive leadership and clear direction.
5. Democratic
Democratic managers encourage team members to take the initiative, question the status quo, make suggestions and collaborate. It’s a participative, or shared, leadership style.
The advantages of democratic management include:
- Efficient decision-making: Democratic managers encourage team members to participate in decision-making, which can help create a sense of investment among employees.
- High employee motivation: Employees may feel more motivated and energized because they are encouraged to take the initiative.
- Increased creativity: Democratic managers allow their employees to come up with ideas, which often leads to increased creativity.
The disadvantages of democratic management include:
- Length of time to make decisions: If team members cannot reach a consensus, decisions may take longer to make.
- Conflict among employees: Because all employees are encouraged to share their ideas and opinions, disagreements are likely.
- Inefficient operations: Democratic managers may experience delays in decision-making, which can result in lags in operations.
The democratic style is best suited for shared leadership that encourages creative thinking and collaboration. This type of management might be helpful when the company has a diverse workforce or no clear leader.
6. Laissez-faire
Laissez-faire leadership describes a hands-off style where the boss allows employees to make their own decisions and often leads by example rather than by providing direct instructions.
The advantages of laissez-faire management include:
- Employee empowerment: Employees who have freedom to make their own decisions often feel more motivated.
- Less micromanaging: Laissez-faire managers create a more relaxed and productive work environment by giving employees more latitude to work at their own pace.
- Innovation: Because employees have the freedom to make their own decisions, they may feel encouraged to think outside the box and develop creative solutions.
The disadvantages of laissez-faire management include:
- Lack of direction among employees: Since there is no clear direction from the manager, employees may feel lost and have difficulty prioritizing.
- Potential indecision issues: Employees are encouraged to share their ideas, which can cause conflict among team members and delay a consensus.
- Lack of productivity: Without clear leadership, employees may not be as productive as possible.
The laissez-faire style is best suited to those looking for a more relaxed work environment where employees are expected to take the initiative. This type of management could be used when a company has a lot of experienced employees or is in a stable state.
7. Pace-setting
Pace-setting managers are usually more direct when communicating with employees and have little tolerance for those who fail to pull their weight in the workplace.
The advantages of pace-setting management include:
- High productivity: Employees might be productive because they feel the pressure to meet high standards.
- Clear expectations: Pace-setting managers set clear expectations for their employees, which helps them stay on track and avoid confusion.
- Discipline: Pace-setting managers might use negative consequences to ensure their employees complete tasks on time and well.
The disadvantages of pace-setting management include:
- Potential employee burnout: Employees who are constantly pressured to meet high standards often burn out.
- Decreased employee motivation: Pace-setting managers may find it challenging to motivate employees in the long run, especially in a company with a diverse workforce.
- Employee resistance: Employees who dislike pressure and high standards might try to avoid challenging assignments or use excuses to get out of work. This can lead to an inefficient workplace culture.
Pace-setting management might be ideal for more traditional work environments at companies that are looking to increase productivity. This type of leadership style might be used when the company is expanding or has a lot of new employees.
8. Visionary
Visionary managers encourage employees to be proactive and take the initiative, and they try to inspire a generally positive attitude in the workplace. They believe in empowering their employees and giving them enough information to make informed decisions while letting go of control when necessary.
The advantages of visionary management include:
- Employee empowerment: Employees who can be proactive and make decisions often feel more valued.
- A sense of employee ownership: By taking on responsibility for decisions, employees feel more invested in the company and are less likely to leave.
- Efficient decision-making: With enough information, employees may make decisions without waiting for approval. This can help companies save time and improve efficiency.
The disadvantages of visionary management include:
- Potential for poor employee choices: When employees are empowered, they may make more mistakes due to a lack of experience.
- Potential employee resentment: Employees who are not allowed to contribute may resent their managers. This can lead to decreased productivity and an unhealthy work environment.
Visionary management might be found at companies looking to develop a proactive and positive work culture. This type of management could be used when the company is a startup or has recently undergone changes.
Finding the best management style
Mastering management skills is one of many essential tips for successfully starting a business, but entrepreneurs aren’t the only people who benefit. Employees may become leaders down the road, and they’ll take their management style cues from their managers and mentors. Finding the best style will come with trial and error, and it may end up shifting down the line as team composition changes.
One of the best things about the different styles of management is flexibility. Combine approaches to create a management style that works best. These styles are not one size fits all, so it’s important to find the one that works best for the individual and company — and maybe customize it to objectives.
Take the first step toward developing a management style
Discovering and developing a management style can begin with a good foundation of business skills. University of Phoenix offers business programs that include:
- General Management Certificate
- Certificate in Leadership and Management
- Project Management Certificate (Undergraduate)
- Human Resource Management Certificate
- Associate of Arts with a concentration in Business Fundamentals
- Bachelor of Science in Business
- Bachelor of Science in Management Degree
- Master of Management
- Master of Business Administration
No one likes a manager who micro-manages. Find out how to avoid becoming that manager by watching the video How to Avoid Micromanaging Employees.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
A graduate of Johns Hopkins University and its Writing Seminars program and winner of the Stephen A. Dixon Literary Prize, Michael Feder brings an eye for detail and a passion for research to every article he writes. His academic and professional background includes experience in marketing, content development, script writing and SEO. Today, he works as a multimedia specialist at University of Phoenix where he covers a variety of topics ranging from healthcare to IT.

ABOUT THE REVIEWER
Currently Dean of the College of Business and Information Technology, Kathryn Uhles has served University of Phoenix in a variety of roles since 2006. Prior to joining University of Phoenix, Kathryn taught fifth grade to underprivileged youth in Phoenix.
This article has been vetted by University of Phoenix's editorial advisory committee.
Read more about our editorial process.
Read more articles like this: